- Home
- Medical Technology
- Laparoscopic Surgery with Small Incision
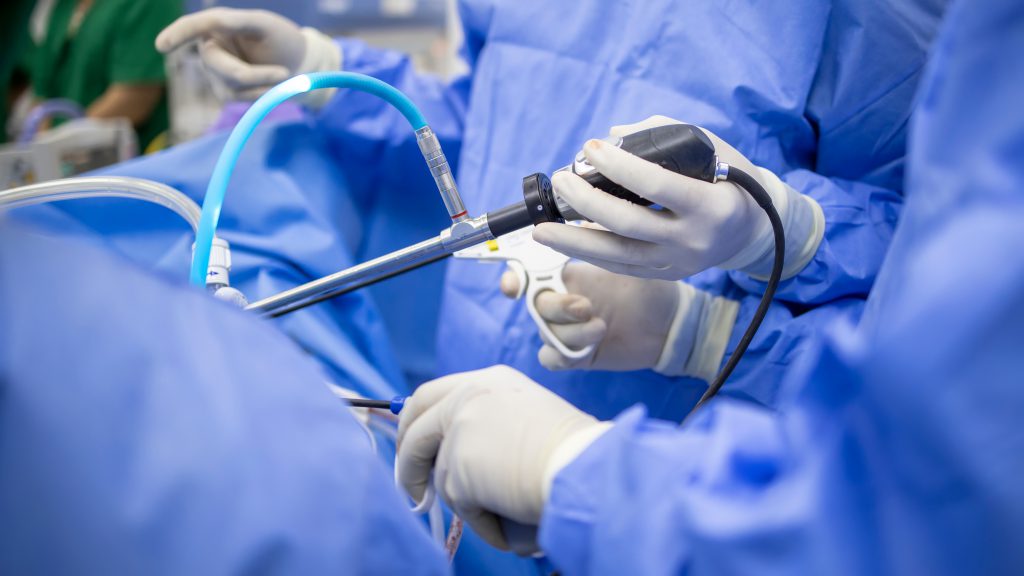
Laparoscopic surgery refers to an innovative surgery that slightly affects the nearby organs with less blood and only a small injury or no external wounds at all. The chance of disease or complications is also reduced without hospitalization for many nights, making it possible to return to normal life faster. This surgery greatly reduces the anxiety of patients and relatives.
Small wound surgery for many diseases
Minimally Invasive Surgery (MIS) causes significantly slight damage to the nearby organs since the surgeon would construct a small hole about 0.5 cm. for 3 spots and 1 cm on the abdomen around the navel, or depending on the organ to insert a camera and surgical tools through the abdominal wall. The surgeon would see the organ through a large screen, making it possible to clearly see the surgery area. Therefore, this provides high accuracy and can also be done with many diseases, such as gallstones, appendix, hernia, diseases related to the colon, stomach, or even diseases of the internal organs of women, such as chocolate cysts and ovarian and uterine tumors. Laparoscopic surgery is a suitable alternative for those mentioned above.
Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy
Once a hole is created and a tool is inserted into the abdomen, the surgeon will remove the gallbladder from the liver through the hole in the navel area. The surgeon will use clips to stop bleeding instead of sutures. After the surgery is complete, the wound on the abdominal surface will be sutured. Hence, the wound is small and less painful.
Laparoscopic Appendectomy
The surgeon inserts a surgical tool through the hole and removes the appendix using a camera as a navigator. But if the surgeon finds that the appendix has ruptured or there is inflammation of the peritoneum caused by infection, an open surgery may be employed instead of a laparoscopic surgery depending on the severity and risks assessed from the health of the patient.
Pros of Laparoscopic Surgery
- Incision size is as small as 1-2 cm while open-technique surgery results in a wound width of 12-20 cm.
- The surgeon can clearly see the components of the desired surgery location with the magnification of the camera, leading to precision in surgery and reducing the impact on other organs.
- Injuries to tissues and internal organs from the surgery are reduced, leading to minor pain and blood loss as well as faster recovery.
- Complications and abdominal adhesions from open surgery are reduced.
- Recover at the hospital takes only 1-2 days. In some cases, patients may return home immediately after surgery. This is faster than open surgery which requires weeks of recovery.
- Laparoscopic surgery is safer than open technique abdominal surgery.
Limitation of Laparoscopic Surgery
- Cost is relatively high due to the need for special equipment while faster recovery is the outcome, thus reducing the cost of hospitalization.
- Laparoscopic surgery cannot be performed for some patients, such as patients with severe lung and heart disease or those who have undergone surgery and have plenty of abdominal adhesion.
เมื่อคุณเข้าชมเว็บไซต์ใดก็ตาม ไซต์นั้นอาจจัดเก็บหรือดึงข้อมูลจากเบราว์เซอร์ของคุณ ส่วนใหญ่แล้วอยู่ในรูปแบบของคุกกี้ ข้อมูลนี้อาจเกี่ยวกับคุณ การตั้งค่าของคุณ อุปกรณ์ของคุณ หรือเพื่อช่วยให้ไซต์ทำงานอย่างที่คุณต้องการ ซึ่งมักเป็นข้อมูลที่ไม่สามารถระบุตัวตนของคุณได้โดยตรง แต่ช่วยให้คุณใช้งานเว็บตามความต้องการส่วนบุคคลได้มากยิ่งขึ้น ท่านสามารถศึกษาข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมได้ที่ นโยบายคุกกี้ (Cookie Policy) และ นโยบายความเป็นส่วนตัว (Privacy Policy)
การใช้งานเว็บไซต์นี้เป็นการยอมรับข้อกำหนดและยินยอมให้เราจัดเก็บคุกกี้ตามนโยบายที่แจ้งในเบื้องต้น
ศูนย์การตั้งค่าความเป็นส่วนตัว
ความเป็นส่วนตัวของคุณ
เมื่อคุณเข้าชมเว็บไซต์ใดก็ตาม ไซต์นั้นอาจจัดเก็บหรือดึงข้อมูลจากเบราว์เซอร์ของคุณ ส่วนใหญ่แล้วอยู่ในรูปแบบของคุกกี้ ข้อมูลนี้อาจเกี่ยวกับคุณ การตั้งค่าของคุณ อุปกรณ์ของคุณ หรือเพื่อช่วยให้ไซต์ทำงานอย่างที่คุณต้องการ ซึ่งมักเป็นข้อมูลที่ไม่สามารถระบุตัวตนของคุณได้โดยตรง แต่ช่วยให้คุณใช้งานเว็บตามความต้องการส่วนบุคคลได้มากยิ่งขึ้น ท่านสามารถศึกษาข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมได้ที่ นโยบายคุกกี้ (Cookie Policy) และ นโยบายความเป็นส่วนตัว (Privacy Policy)
การใช้งานเว็บไซต์นี้เป็นการยอมรับข้อกำหนดและยินยอมให้เราจัดเก็บคุกกี้ตามนโยบายที่แจ้งในเบื้องต้น
คุกกี้เหล่านี้จำเป็นสำหรับการทำงานกับเว็บไซต์ และไม่สามารถปิดการใช้งานในระบบของเราได้ และโดยปกติแล้ว คุกกี้เหล่านี้จะถูกกำหนดไว้เพื่อตอบสนองต่อการดำเนินการร้องขอบริการของคุณ เช่น การตั้งค่าความเป็นส่วนตัว การเข้าสู่ระบบ หรือการกรอกแบบฟอร์ม คุณสามารถกำหนดให้เบราว์เซอร์ของคุณทำการบล็อก หรือเตือนให้คุณทราบเกี่ยวกับคุกกี้เหล่านี้ แต่นั่นอาจทำให้บางส่วนของไซต์ไม่สามารถทำงานได้
คุกกี้เหล่านี้ช่วยในการทำงานของไซต์และการปรับแต่งไซต์ให้เหมาะกับผู้ใช้ เช่น วิดีโอและการสนทนาสด คุกกี้เหล่านั้นอาจได้รับการกำหนดโดยเราหรือผู้ให้บริการจากบริษัทอื่นที่เราได้เพิ่มบริการของพวกเขาลงในหน้าเพจ หากคุณไม่อนุญาตให้คุกกี้เหล่านี้ทำงาน ฟังก์ชันบางอย่างของไซต์อาจทำงานไม่ถูกต้อง
คุกกี้เหล่านี้ช่วยเราในการนับจำนวนและที่มาของการเข้าชม เพื่อให้เราสามารถวัดและปรับปรุงประสิทธิภาพไซต์ของเราได้ นอกจากนี้ยังช่วยให้เราทราบว่าหน้าใดได้รับความนิยมมากที่สุดและน้อยที่สุด และทราบว่าผู้เยี่ยมชมเข้าดูส่วนใดบ้าง ข้อมูลทั้งหมดที่คุกกี้เหล่านี้จัดเก็บไว้จะถูกรวมไว้ด้วยกัน จึงทำให้ไม่สามารถระบุตัวตนได้ หากคุณไม่อนุญาตให้คุกกี้เหล่านี้ทำงาน เราจะไม่ทราบว่าคุณเข้าชมไซต์ของเราเมื่อใด
โรงพยาบาลวิชัยเวชหนองแขมได้มีการใช้เทคโนโลยี Google Analytics และ Facebook Pixel ซึ่งมีวัตถุประสงค์เพื่อใช้เก็บข้อมูลเชิงลึกเกี่ยวกับรูปแบบการใช้งานของคุณบนเว็บไซต์ของเรา โดยข้อมูลนี้ประกอบไปด้วย หน้าเว็บไซต์ที่คุณเข้าชม ลิงค์ที่คุณคลิก ระยะเวลาที่คุณเข้าชมแต่ละหน้า โดยเราใช้ข้อมูลนี้เพื่อวิเคราะห์รูปแบบการใช้งานของผู้ใช้ และเพื่อให้เว็บไซต์ทำงานได้อย่างถูกต้อง เราขอยืนยันว่าจะไม่ใช้ข้อมูลนี้เพื่อการตลาดหรือการโฆษณา และจะไม่เปิดเผยกับบุคคลที่สามแต่อย่างใด
คุกกี้เหล่านี้จะถูกกำหนดผ่านไซต์ของเราโดยพาร์ทเนอร์โฆษณาของเรา โดยบริษัทดังกล่าวอาจใช้คุกกี้เหล่านี้เพื่อสร้างโปรไฟล์เกี่ยวกับความสนใจของคุณ และแสดงโฆษณาที่คุณสนใจบนไซต์อื่นๆ คุกกี้เหล่านี้ทำงานโดยการระบุแต่ละเบราว์เซอร์และอุปกรณ์ของคุณ หากคุณไม่อนุญาตให้คุกกี้เหล่านี้ทำงาน คุณจะไม่เห็นโฆษณาที่คุณเป็นเป้าหมายบนเว็บไซต์ต่างๆ
คุกกี้เหล่านี้ได้รับการกำหนดโดยบริการโซเชียลมีเดียที่เราได้เพิ่มบนไซต์ เพื่อช่วยให้คุณสามารถแบ่งปันเนื้อหากับเพื่อนๆ และเครือข่ายของคุณได้ คุกกี้เหล่านี้สามารถติดตามเบราว์เซอร์ของคุณเมื่อเข้าชมไซต์อื่นๆ และสร้างโปรไฟล์เกี่ยวกับความสนใจของคุณได้ ซึ่งจะส่งผลต่อเนื้อหาและข้อความที่คุณเห็นบนเว็บไซต์อื่นๆ ที่คุณเข้าชม หากคุณไม่อนุญาตให้คุกกี้เหล่านี้ทำงาน คุณจะไม่สามารถใช้หรือดูเครื่องมือการแบ่งปันเหล่านี้ได้